
The total amount of depreciation taken over the entire life of the asset should equal the depreciable cost (cost minus salvage value). You can manually adjust the depreciation expense taken to equal the depreciable cost, or you can include additional formulas to make sure that the total depreciation equals the depreciable cost. If you are interested, these additional formulas are included in the Excel workbook and produce the results shown in the screenshot below.
How can linear depreciation be calculated?
Without further ado, allow me to simplify this concept to enlighten you wonderfully. 36A linear function used to describe the declining value of an item over time. This indicates that when \(50\) units are produced and sold the corresponding profit is a loss of \($880\). Obtain the profit function by subtracting the cost function from the revenue function. The value of the item depends on the number https://www.bookstime.com/blog/restaurant-cash-flow-management of years after it was purchased. Therefore, the age of the piece of equipment is the independent variable.
Understanding Linear Depreciation: Definition, Calculation, and Application

In addition to straight line depreciation, there are also other methods of calculating depreciation of an asset. Different methods of asset depreciation are used to more accurately reflect the depreciation and current value of an asset. A company may elect to use one depreciation method over another in order to gain tax or cash flow advantages. To calculate the straight line basis, take the purchase price of an asset and then subtract the salvage value, its estimated value when it is no longer expected to be needed.
- The total cost of renting the truck for the day and driving it \(60\) miles would be \($75\).
- It is calculated by subtracting an asset’s salvage value from its current value and dividing the result by the number of years until it reaches its salvage value.
- Companies use depreciation for physical assets, and amortization for intangible assets such as patents and software.
- When you purchase an asset, you usually can’t write off the entire cost on your taxes in the year you bought it.
What Are Realistic Assumptions in the Straight-Line Method of Depreciation?
This depreciation method is appropriate where economic benefits from an asset are expected to be realized evenly over linear depreciation function its useful life. Straight-line depreciation is a simple method for calculating how much a particular fixed asset depreciates (loses value) over time. This means that the company would record a depreciation expense of $2,000 for each year of the equipment’s useful life.

As buildings, tools and equipment wear out over time, they depreciate in value. Being able to calculate depreciation is crucial for writing off the cost of expensive purchases, and for doing your taxes properly. The world of business is complex, especially considering the technical terms used. To light the way, it’s a term that implies the equal depreciation of assets over their useful life.

Accounting Purposes
- Round up because the number of units produced and sold must be an integer.
- The IRS has a useful system known as the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS), which is sometimes represented as a table.
- Your financial statements are more than a look at how your business performed in the past.
- Many accountants use a simple, easy-to-use method called the straight-line basis.
- These numbers can be arrived at in several ways, but getting them wrong could be costly.
- To see this, calculate the profit where \(n\) is \(139\) and \(140\) units.
- In addition to an initial setup fee of \($120\), each t-shirt cost \($3.50\) to produce.
For example, due to rapid technological advancements, a straight line depreciation method may not be suitable for an asset such as a computer. A computer would face larger depreciation expenses in its early useful life and smaller depreciation expenses in the later periods of its useful life, due to the quick obsolescence of older technology. It would be inaccurate to assume a computer would incur the same depreciation expense over its entire useful life. The DDB function is https://www.facebook.com/BooksTimeInc/ used for calculating double-declining-balance depreciation (or some other factor of declining-balance depreciation) and contains five arguments. The first four (cost, salvage, life, and period) are required and the same as used in the DB function. The fifth argument, factor, is optional and determines by what factor to multiply the rate of depreciation.
- 38Using a linear function to estimate values that extend beyond the given data points.
- 42The point at which profit is neither negative nor positive; profit is equal to zero.
- Compared to the other three methods, straight line depreciation is by far the simplest.
- The DDB function is used for calculating double-declining-balance depreciation (or some other factor of declining-balance depreciation) and contains five arguments.
Salvage Value
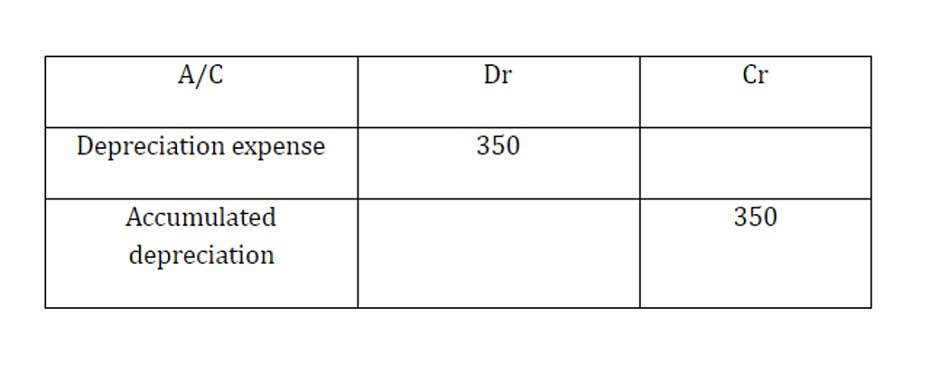
However, depreciation can be calculated for other contexts using the same basic steps. In finance, a straight-line basis is a method for calculating depreciation and amortization. It is calculated by subtracting an asset’s salvage value from its current value and dividing the result by the number of years until it reaches its salvage value. This is relatively easy to identify in physical assets you’ve purchased, but it can be a bit more complicated for other types of assets. The estimates of useful life or residual value of an asset may need to be revised in subsequent accounting periods in order to reflect more accurately the pattern of economic benefits in light of new information. Straight line depreciation method charges cost evenly throughout the useful life of a fixed asset.
- The value of the item depends on the number of years after it was purchased.
- To light the way, it’s a term that implies the equal depreciation of assets over their useful life.
- The double-declining balance method results in higher depreciation expenses in the beginning of an asset’s life and lower depreciation expenses later.
- Different methods of asset depreciation are used to more accurately reflect the depreciation and current value of an asset.
- It calculates how much a specific asset depreciates in one year, and then depreciates the asset by that amount every year after that.
- Straight line depreciation is, in general, considered the default method for calculating the depreciation of assets.
- From the graph we can determine two points \((−1, −2)\) and \((4, 1)\).
ways to calculate depreciation in Excel
You can access the two accompanying videos here and here and a workbook with examples of using the various depreciation methods. These eight depreciation methods are discussed in two sections, each with an accompanying video. The first section explains straight-line, sum-of-years’ digits, declining-balance, and double-declining-balance depreciation.